유형별 문제 풀이 - 고급 자료구조 - 03. 핵심 유형 문제풀이
-> 문제유형 : 그래프, 해시, 집합, 유니온 파인드
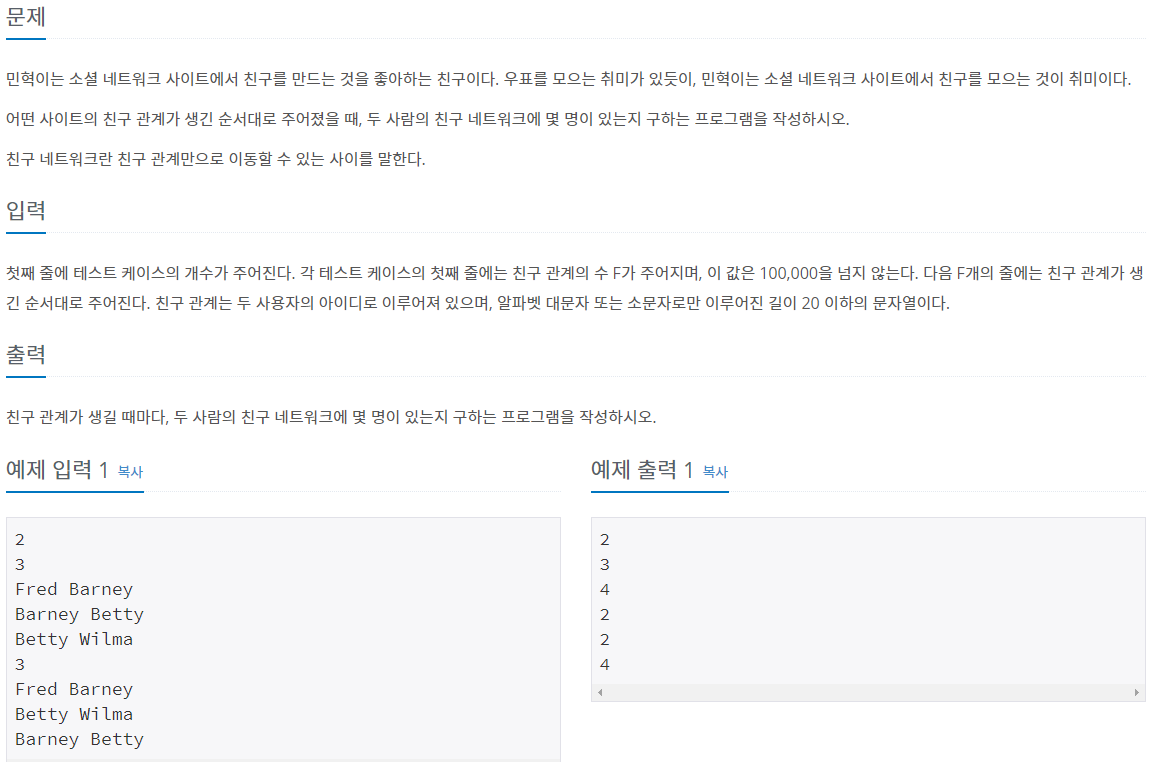
import sys
input = sys.stdin.readline
def FindRoot(x):
if x == parent[x]:
return x
else:
p = FindRoot(parent[x])
parent[x] = p
return parent[x]
def Union(a,b):
x = FindRoot(a)
y = FindRoot(b)
if x != y:
parent[y] = x
number[x] += number[y]
tc = int(input())
for _ in range(tc):
num = int(input())
parent = {}
number = {}
for _ in range(num):
x,y = list(input().split())
if x not in parent:
parent[x] = x
number[x] = 1
if y not in parent:
parent[y] = y
number[y] = 1
Union(x,y)
print(number[FindRoot(x)])
-> 문제유형 : 해시, 배열, 구현
point. 특정 정수의 등장 여부만을 체크하면 된다면 set이나 dictionary를 사용하라 -> 여기서는 key값만 필요하고 value값은 필요없으니 set으로
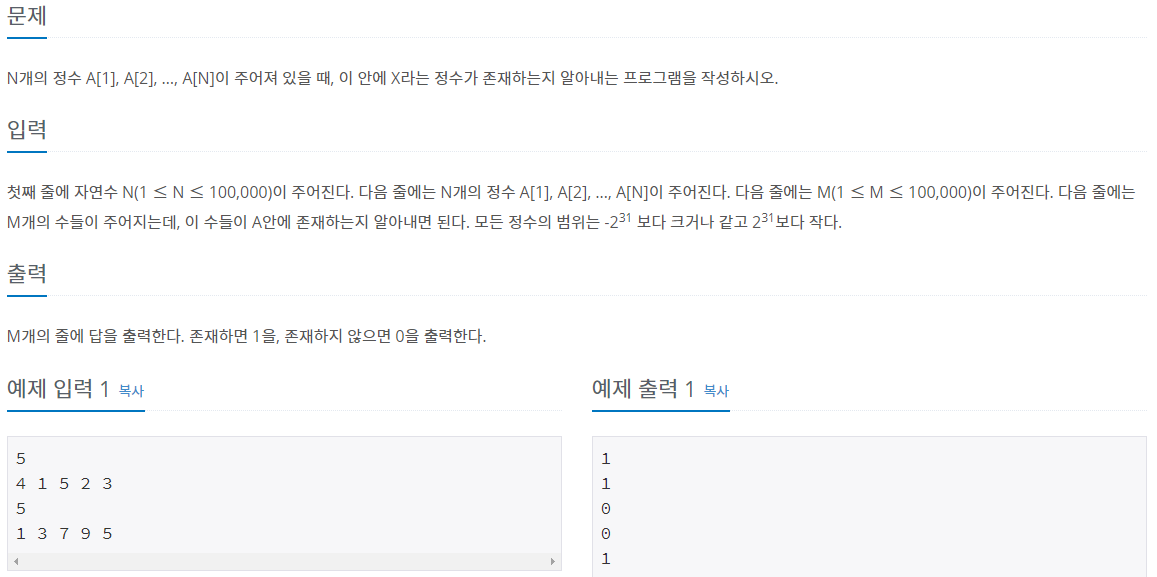
n = int(input())
array = set(map(int, input().split()))
m = int(input())
m_list = list(map(int,input().split()))
for i in m_list:
if i in array:
print(1)
else:
print(0)※ dictionary : 키와 값을 값는 데이터 구조, 키는 내부적으로 hash 값으로 저장됨
※ set : dictionary에서 key만 활용하는 데이터 구조, 수학에서 집합과 도일한 개념
# 10930 SHA-356 (브론즈2)
-> 문제유형 : 해시, 구현
import hashlib
input_data = input()
encoded_data = input_data.encode()
result = hashlib.sha3_256(encoded_data).hexdigest()
print(result)
반응형
'알고리즘 > baekjoon' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [백준/파이썬] 나이순 정렬, 좌표 정렬하기, 수 정렬하기3 (0) | 2021.06.21 |
|---|---|
| [백준/파이썬] 수 정렬하기, 소트인사이드 (0) | 2021.06.20 |
| [ 백준 / 파이썬 ] 20058 마법사 상어와 파이어스톰 (0) | 2021.06.12 |
| [ 백준 / 파이썬 ] 21608 상어 초등학교 (0) | 2021.06.12 |
| [ 백준 / 파이썬 ] 20057 마법사 상어와 토네이도 (0) | 2021.06.11 |